Banking: Commercial Banks and the Central Bank
Contents
RBI regulates the interest rate on NRI deposits, export credits , and a few other categories. However, the interest rate on most of the categories of deposit and lending have been deregulated so the banks are responsible for determining such rates. RBI acts as an advisor to the government when called upon to do so on financial and banking-related matters.
- To safeguard the interest of every investor and offer economic and cost-efficient services to the public.
- Central Bank succeeds in convincing the banks as it acts as the lender of last resort however no punitive action is taken in case they do not follow the advice or request.
- Thus the ability to convert an asset into money/cash quickly and without loss of value is called liquidity of asset.
- So, here we will read in detail about these three types of functions.
- A major objective of the RBI is to support the planned advancement of the country’s economy.
- The debt management policy mainly aims at minimizing the cost of borrowing and smoothening the maturity structure of debt.
RBI is also an official reservoir of foreign currencies and gold. RBI sells gold to monetary authorities of other countries at fixed prices. As per law, commercial banks need to keep a reserve that is equal to a certain percentage of the NDTL . These reserves help commercial banks clear cheques by transferring funds from one bank to another.
The Reserve Bank’s affairs are governed by a central board of directors. The Central Board of Directors is the apex body in the governance structure of the Reserve Bank. There are also four Local Boards for the Northern, Southern, Eastern and Western areas of the country which take care of local interests. The central government appoints/nominates directors to the Central Board and members to the Local Boards in accordance with the Reserve Bank of India Act. The composition of the Central Board is enshrined under Section 8 of the RBI Act, 1934. The debt management policy mainly aims at minimizing the cost of borrowing and smoothening the maturity structure of debt.
Objectives of RBI
However as the transactions increased, inconveniences and difficulties of barter exchange also increased involving rising trading costs. Trading costs are nothing but costs of engaging in trade. Its two components are – search cost and disutility of waiting. Remember, search cost is the high cost of searching suitable persons to exchange goods and disutility of waiting refers to time period spent on searching the required person. This ultimately led to evolution of money as medium of exchange. It has been mentioned above that a Central Bank is the custodian of foreign exchange resources and nation’s gold.
Department of Administration and Personnel Management. Q.24. Describe the prohibited functions of Reserve Bank of India. Also, you can read the SCERT book online in these sections Solutions by Expert Teachers as per SCERT Book guidelines.
The central bank is the organ of the government which controls major financial operations of the government. Through its various operations, the objectives of the central bank are to support the economic policy of a country by influencing the way financial institutions behave. The Reserve Bank has adopted the Minimum Reserve System for issuing/printing the currency notes. Since 1957, it maintains gold and foreign exchange reserves of Rs. 200 Cr. Should be in gold and remaining in the foreign currencies.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI): History, Objectives and Functions
Suppose initial deposit of Rs 10,000 is received by bank and LRR is assumed to be 10%. So the bank will keep 10% of as Reserves i.e 1,000 and will lend remaining 9000 Some Borrower who are free to withdraw this amount anytime. Collection of Statistics- banks collect and publish statistics relating to trade commerce and industry. 2) Discounting functions of rbi class 12 Bills of Exchange- It refers to a facility where a holder of a bill of exchange can get the bill discounted before dating of maturity. For providing the service Bank deduct some Commission out of the total amount of bill of exchange. Adding the date of maturity, the bank received his payment from the 2nd partner who accepts the bill.
The central bank is given the sole monopoly of issuing currency in order to secure control over volume of currency and credit. These notes circulate throughout the country as legal tender money. Note-issuing is governed by Minimum Reserve System i.e. while issuing currency notes, a minimum fixed amount of gold and foreign currency is kept by Central Bank.
Should you have any queries, you can get in touch with our course counselors to seek assistance. According to the current trends, as many as 16% of the total questions from the Finance section are asked from RBI and https://1investing.in/ monetary policy. Read it at length, as it is important for both Prelims and the Main exam. Our training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship.
Banking Functions
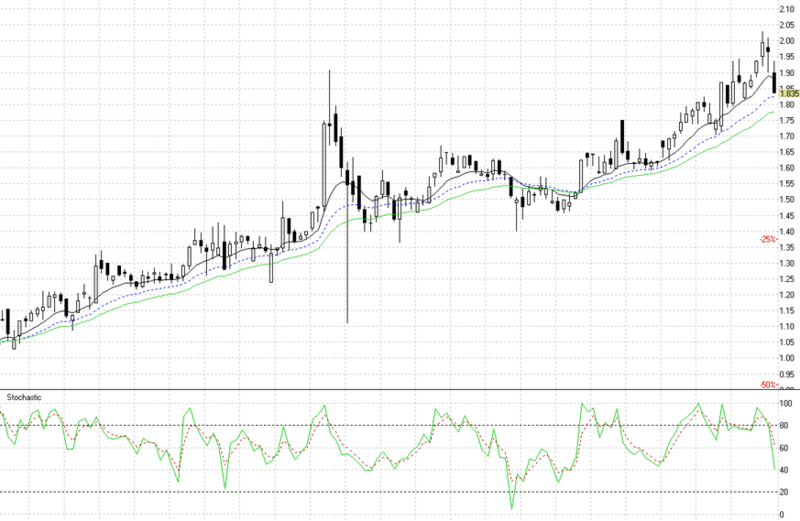
It may be noted that liquidity means ability to convert an asset into money quickly and without loss of value. According to government of India ‘Economic Survey 2004’, the position of M3on March 31, 2004 was as under. The Reserve bank of India controls the credit created by commercial banks. The credit flow in the country is regulated by means of two methods; quantitative method and qualitative method.
DICGC covers all commercial banks including foreign bank branches as well along with UCBs/StCBs/DCCBs. But it is important to note that it does not cover deposits of foreign governments, deposits of Central and State governments, and interbank deposits. A country’s overall economy and steadiness are based on the payment and settlement mechanisms operating in that nation.
These solutions are part of SCERTAll Subject Solutions. Here we have given Class 12 Banking Chapter 2 Reserve Bank Of India Solutions for All Subjects, You can practice these here. The loan book has grown to nearly four times as much, at Rs2.25 trillion as on September 30, 2019. Since then, the loan book has grown to nearly four times as much, at Rs 2.25 trillion as on September 30, 2019. Analysts believed the new management of YES Bank, headed by former Deutsche Bank India head Ravneet Gill, who joined the bank in early 2019, could turn around the ship.
This department will also perform the duties of developing and monitoring the instruments of the money market and also monitoring the government securities and foreign money markets. It refers to the minimum percentage of total deposits to be kept by commercial banks with themselves. Open Market Operations- It refers to buying and selling of government securities to or from the general public or commercial bank. All Central Bank who is the Reserve of all commercial bank, it becomes easy and more convenient for it to act as their clearinghouse. All commercial banks have their account with Central Bank. Therefore the central bank can easily set with claims of various commercial banks against each other.
Class 12 Banking Chapter 7 পুঁজি নিয়োগ
Even if the central government does not own a central bank, the law establishes and protects the privileges of a central bank. Most central banks are centralized though there could be central banks that are not government agencies. Extending banking services to semi-urban and rural areas.
If Bank Rate increase, banks will have to pay more int to Central Bank. Oliveboard is a learning & practice platform for premier entrance exams. We have helped over 1 crore users since 2012 with their Bank, SSC, Railways, Insurance, Teaching and other competitive Exams preparation. So it can be concluded that as soon as our country is growing the role of RBI is going to be very crucial in the upcoming years. Initially, the ownership of almost all the share capital was in the hands of non-government shareholders.
Money serves as unit of account or a measure of value. Money is the measuring rod, i.e., it is the unit in which the values of other goods and services are measured in terms of money and expressed accordingly. Different goods produced in the country are measured in different units, e.g., cloth in metres, milk in litres, sugar in kilograms. Without a common unit of measure, exchange of goods and services becomes very difficult. Values of all goods and services can be expressed in a single common unit called money.
There is a separate department operated by the central bank in big cities and trade centers to transfer and settle the claims of one bank on the other. When commercial banks have exhausted all resources to supplement their funds at times of liquidity crisis, they approach Central Bank as a last resort. This saves banks from possible failure and banking system from a possible breakdown.
Again it helps to make contracts which involve future payments. Money as measure of value or a unit of account solves the barter problem of lack of common measure of value. Money measures exchange value of commodities and makes keeping of business accounts possible. Money, thus, acts as common medium of exchange, a common measure of value, as stamlard of deferred payments and a store of value. Another Function ‘Liquidity of Money’ is added these days. Thus the ability to convert an asset into money/cash quickly and without loss of value is called liquidity of asset.